Wikipedia Probability Of Poker Hands
Thus there are C(52, 5) = 2598960 different hands. The poker sample space consists of 2598960 equally probable elementary events. The probability of whichever hand is naturally 1/2598960. 81-82 shows another elegant way of arriving at the same probability. Imagine having a urn with 52 balls, of which 5 are black and the remaining white.
- Wikipedia Probability Of Poker Hands Free
- Wikipedia Probability Of Poker Hands Game
- Poker Hands Probability Chart
- Calculating Probability Of Poker Hands
- Probability Of Poker Hands
- Poker Hands Probability Wiki
Wikipedia Probability Of Poker Hands Free
Poker dice are dice which, instead of having number pips, have representations of playing cards upon them. Poker dice have six sides, one each of an Ace, King, Queen, Jack, 10, and 9, and are used to form a poker hand.
Each variety of poker dice varies slightly in regard to suits, though the ace of spades is almost universally represented. 9♣ and 10♦ are frequently found, while face cards are traditionally represented not by suit but instead by color: red for kings, green for queens and blue for jacks. Manufacturers have not standardized the colors of the face sides. The game can also be played with ordinary dice.
As a game[edit]
The classic poker dice game is played with 5 dice and two or more players. Each player has a total of 3 rolls and the ability to hold dice in between rolls. After the three rolls, the best hand wins.
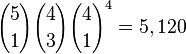
In most variations, a straight only counts as a Bust (high-card). A Straight is less probable than a Full House, so, if counted, it should rank above a Full House, though tradition usually ranks it below Full House, as in card poker. Neither a 'flush' nor a 'straight flush' is a possible hand, due to the lack of suits on the dice.
In some rules, only a straight to a King is called a Straight, while a straight to an Ace is called (somewhat incorrectly) a Flush. Each one has an exact probability of 120 / 7776. Under these rules, a Straight beats a Full House (unlike in card poker, but correctly reflecting its probability) but does not beat Four of a Kind (incorrectly reflecting its lower probability). A Flush beats Four of a Kind (as in card poker, and correctly reflecting its lower probability).
Probabilities[edit]
The poker dice hand rankings and the corresponding probabilities of rolling that hand are as follows[1][2](not sorted by probability but from highest to lowest ranking):
| Hand | Exact probability | Percentage | 1 in ... | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Five of a kind | 6 / 7776 | 0.08% | 1296 | J J J J J |
| Four of a kind | 150 / 7776 | 1.93% | 51.8 | 10 10 10 10 A |
| Full house | 300 / 7776 | 3.86% | 25.9 | K K K 9 9 |
| Straight | 240 / 7776 | 3.09% | 32.4 | A K Q J 10 |
| Three of a kind | 1200 / 7776 | 15.43% | 6.5 | 9 9 9 K J |
| Two pair | 1800 / 7776 | 23.15% | 4.3 | Q Q 9 9 A |
| One pair | 3600 / 7776 | 46.30% | 2.2 | 10 10 K Q 9 |
| Bust (high card; no pair, no straight) | 480 / 7776* | 6.17% | 16.2 | A K Q J 9 |
*Busts have much lower probability than in card poker, because there are only 6 values instead of 13, making pairs and straights much more likely than with cards. In poker dice there are in fact only four possible bust hands: [A K Q J 9], [A K Q 10 9], [A K J 10 9], and [A Q J 10 9]; both other no-pair hands (i.e., in which either the A or the 9 are missing) are straights. Consequently, in some variants of the rules, straights are counted as busts.[3]
Variants[edit]
Marlboro once marketed a set of octahedral poker dice that included suits; each die had slightly different numberings, ranging from 7 up to ace. A similar set is currently manufactured by Koplow Games.[4][5]
In 1974 Aurora produced a set of 12-sided poker dice called 'Jimmy the Greek Odds Maker Poker Dice'[6] and in 2000 Aurora/Rex Games produced a similar set under the name 'Royal Poker Dice'.[7] The sets featured five 12-sided dice allowing for all 52 playing cards to be represented. The remaining 8 faces featured stars and acted as wild cards allowing for every possible poker hand to be rolled.
See also[edit]
Wikipedia Probability Of Poker Hands Game
References[edit]
Poker Hands Probability Chart
- ^Deep, Ronald (2006), Probability and statistics with integrated software routines, Elsevier Inc., ISBN0-12-369463-9Chapter 1 p 42
- ^Bărboianu, Cătălin (2006), Probability Guide to Gambling: The Mathematics of Dice, Slots, Roulette, Baccarat, Blackjack, Poker, Lottery and Sport Bets, INFAROM Publishing, p. 224, ISBN973-87520-3-5Extract of page 224
- ^Arneson, Erik (2012). 'The Complete Rules for the Dice Game Poker Dice'. About.com. New York Times Company. 'Board / Card Games' subsite. Archived from the original on 2014-04-12.CS1 maint: unfit url (link)
- ^Koplow Games
- ^8-sided poker dice on BoardGameGeek.com
- ^Jimmy the Greek Odds Maker Poker Dice on BoardGameGeek.com
- ^Royal Poker Dice on BoardGameGeek.com
Calculating Probability Of Poker Hands
External links[edit]

Probability Of Poker Hands
- Rules for Dice Poker at BrainKing.com (similar to Yahtzee)
- Arneson, Erik (2012). 'The Complete Rules for the Dice Game Poker Dice'. About.com. New York Times Company. 'Board / Card Games' subsite. Archived from the original on 2014-04-12.CS1 maint: unfit url (link) (no straights)
- Poker dice at Britannica.com